Size-driven phenomena as origin for novel traits of advanced ferroelectric nanostructured (Ba,Sr)TiO3 ceramics
Project Director: Dr. Roxana Elena Patru
FINANCING CONTRACT NO: PD 133 din 20/08/2020
Code: PN-III-P1-1.1-PD-2019-0739
Project Duration (months): 24
The considerable research interest raised by ferroelectrics has been increasingly directed, in recent years, towards nanostructures, paying special attention mostly to “lead-free” materials. The nanoscale transition has become one of the engines of nowadays research since it made it possible to acquire multi-functionality in many types of materials and structures. The size-dependent electrical properties observed in ferroelectrics have been extensively investigated in un-doped BaTiO3-BT ceramics, and not to the same extent in the related solid solutions. The present project shall perform a complete investigation of the grain size effects on the structural/microstructural and macroscopic functional properties in (Ba, Sr)TiO3-BST, a BT-based solid solution.
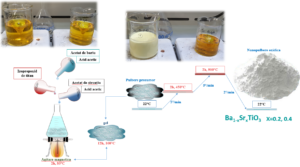
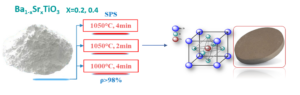
The study will be performed by a multidisciplinary approach, involving innovative wet-chemical methods for the preparation of nanopowders and combined conventional and spark plasma sintering to obtain dense nanostructured BST ceramics of different compositions and grains scales. There are two envisaged BST compositions, in different phase states at room temperature: (i) Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3, in the ferroelectric tetragonal state (PS≠0), and (ii) Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3, in the paraelectric cubic state (PS=0). This research can bring major contributions to clarify the influence of the grain size effects along with interfaces/boundary – related phenomena on the type and characteristics of the ferroelectric-paraelectric phase transition and the structural, thermal, and dielectric properties of BST ceramics of various grain sizes.
The challenge is to understand how the functional properties of bulk BST ceramics are influenced by the grains size and to find the optimal characteristics for specific applications in the microelectronic industry. The results can be used as a foundation for pointing out unanswered issues regarding size-dependent and interfaces/boundary-related phenomena in BST ferroelectrics and paves the way for future improvements.
Project Domains
Main Domain PE. PHYSICAL SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING; Main Subdomain PE5. Synthetic Chemistry and Materials: Materials synthesis, structure-properties relations, functional and advanced materials, molecular architecture, organic chemistry; Main research area PE5_2. Solid-state materials
Secondary Domain PE. PHYSICAL SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING; Secondary Subdomain PE5. Synthetic Chemistry and Materials: Materials synthesis, structure-properties relations, functional and advanced materials, molecular architecture, organic chemistry; Secondary research area PE5_1. Structural properties of materials
Tertiary Domain PE. PHYSICAL SCIENCES AND ENGINEERING; Tertiary Subdomain PE4. Physical and Analytical Chemical Sciences: Analytical chemistry, chemical theory, physical chemistry/chemical physics; Tertiary research area PE4_17. Characterization methods of materials
Keywords: ferroelectrics, micro/nanostructured ceramics, barium strontium titanate, grain-size effects, dielectric properties
Aim of the research
The aim of the research was to investigate ferroelectric ceramics with varying submicron grain sizes in order to highlight the scale effects on ferroelectric functional properties, dielectric properties, and tunability, as well as to highlight the role of intrinsic (decrease in spontaneous polarization, permittivity, and tunability) and extrinsic (intergranular boundaries, defects) effects on them. Essential for obtaining dense nanostructured ceramics with medium particle sizes in the field of interest are to obtain in the first phase quality, non-agglomerated nanopowders with narrow size distribution and to establish an appropriate densification protocol that inhibits grain growth.
Fine-grained BST ceramics were prepared from nanopowders obtained by the sol-gel method and strengthened by plasma spark sintering to inhibit grain growth. Dense, single-phase, and pure ceramics were obtained. By varying the sintering conditions, changes in the grain size of the ceramics were obtained for both investigated compositions, from nanometric to submicron order. The impact of grain size reduction on the dielectric and ferroelectric properties of the obtained dense BST ceramics was investigated over a wide range of frequencies and temperatures using low and high electric field techniques to establish clear correlations between the effect of grain size alone, when no porosity is induced during processing, and the properties of fine-grained BST ceramics.
Project Leader
Ph.D. Roxana Elena Patru; UEF-ID Brainmap Code: U-1700-039N-2562
Mentor
Prof. Ph.D. Eng. Adelina Carmen Ianculescu; UEF-ID Brainmap Code: U-1700-038X-7849
Summary of significant grant achievements
The study of dense Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramics with variable grain size focused mainly on the effect of grain size on structural, morphological, electrical, pyroelectric, and ferroelectric properties, treating with interest in the overlap of tetragonal and cubic phases near room temperature. The cubic to the tetragonal phase transition of nanoscale ceramics is diffuse and flattened, extended over several tens of degrees. By increasing the grain size, an evolution from a 2nd order phase transition to a 1st-order phase transition occurs for submicron ceramics with a low degree of diffusivity. At the same time, the degree of unit cell tetragonality, Curie constant, and field-induced polarization increase with increasing grain size while the conductivity is reduced. A large volume of non-polar regions is present at ambient temperature, which reduces significantly with increasing grain size, confirming the coexistence of tetragonal and cubic phases. The obtained results are highly original and of significant impact, considering that no conclusive studies exist in the literature for this composition and no functional properties of low and high fields at such small grain sizes have been investigated.
The study of dense Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 ceramics with variable grain size focused mainly on the effect of grain size reduction down to the nanoscale on the most important functional properties. Common to all ceramics of this composition is the diffuse character of the phase transition from ferroelectric to paraelectric, with the Curie point set at about 280 K, with a low value of the maximum dielectric permittivity and the presence of dielectric nonlinearity (tunability) and P(E) switching character with low surface area inclined hysteresis loops and low remanent polarization above the Curie point. The permittivity maximum is strongly flattened and, as the grain size decreases, is drastically reduced to a few hundred. Measurements at high fields have shown that the permittivity as a function of the applied electric field changes from butterfly-shaped to thin, but the nonlinearity is still observed even for nanosized ceramics. In addition, while electrical tunability exhibits a linear field dependence, a progressive decrease in tunability occurs with decreasing grain size. Hystereticity reduces with grain size decreases and also with increasing temperature. Although saturation of ferroelectric polarization at room temperature has not been reached even for electric fields up to 70 kV/cm, the energy storage densities determined at this electric field are comparable or even higher than those previously reported for Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 ceramics with micron or submicron grain sizes. However, energy losses at room temperature are high at 70 kV/cm, mainly due to the hysteretic character at high electric fields and the dielectric losses. The energy storage efficiency is about 80% for submicron ceramics and decreases to ~67% for nanometer ceramics. The main advantages of nanostructuring in dense Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 ceramics are (i) reduction of permittivity below 1000 while maintaining an acceptable level of tunability; (ii) linearization of permittivity-field dependence, acquiring reversible and predictable behavior at the expense of butterfly effect; (iii) increased electrostatic energy storage capacity and efficiency due to low hysteretic character, (iv) thermally stable polar nanoclusters above Curie temperature. The original results demonstrate that nanostructuring can make dense electroceramics a successful candidate in microwaves and tunable devices.
1 Structural, functional properties and enhanced thermal stability of bulk graded (Ba,Sr)TiO3 structures obtained by spark plasma sintering (published article)
Authors: Mihaela Botea, Ioana Pintilie, Vasile-Adrian Surdu, Cătălina-Andreea Stanciu, Roxana-Doina Truşcă, Bogdan Ştefan Vasile, Roxana Patru, Mircea Udrea, Adelina-Carmen Ianculescu, Lucian Pintilie
Corresponding authors: Adelina Carmen Ianculescu and Lucian Pintilie
Study: Boundary phenomena and pyroelectric properties in Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramics in a compositionally graded architectural context
Journal of Materials Research and Technology, Volume 12, May–June 2021, Pages 2085-2103, Impact factor: 6.267 (2021) Article influence score: 0.297 (2021)
2 Grain size-driven effect on the functional properties in Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 ceramics consolidated by spark plasma sintering (article accepted for publication with minor revision)
Authors: Roxana-Elena Patru, Catalina Andreea Stanciu, Elena Mirabela Soare, Valise-Adrian Surdu, Roxana Doina Trusca, Adrian Ionut Nicoara, Bogdan Ştefan Vasile, Andra Georgia Boni, Luminita Amarande, Nadejda Horchidan, Lavinia Curecheriu, Liliana Mitoseriu, Lucian Pintilie, Ioana Pintilie, Adelina Carmen Ianculescu
Corresponding authors: Roxana Elena Pătru and Adelina Carmen Ianculescu
Study: Influence of grain size on low and high field functional properties in dense nanostructured Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 ceramics
Journal of the European Ceramic Society, Manuscript Number: JECESOC-D-22-03143, Impact factor: 6.364 (2021) Article influence score: 0.762 (2021)
3 In search of the size-driven phase co-existence in ferroelectric Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 electroceramics (article in process for journal submission)
Authors: Roxana-Elena Patru, Catalina Andreea Stanciu, Elena Mirabela Soare, Valise-Adrian Surdu, Roxana Doina Trusca, Adrian Ionut Nicoara, Nadejda Horchidan, Lavinia Curecheriu, Liliana Mitoseriu, Lucian Trupina, Lucian Pintilie, Ioana Pintilie, Adelina Carmen Ianculescu
Corresponding authors: Adelina Carmen Ianculescu and Ioana Pintilie
Study: Influence of grain size on low and high field functional properties in dense nanostructured Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 ceramics
The paper will be submitted for publication to the Journal of the European Ceramic Society (Impact factor: 6.364, Article influence score: 0.762) or Ceramics International (Impact factor: 5.532, Article influence score: 0.552).
4 Electrical transport phenomena in nanostructured BST dense electroceramics (article in progress)
Authors: Roxana-Elena Patru, Catalina Andreea Stanciu, Valise-Adrian Surdu, Bogdan Ştefan Vasile, Roxana Doina Trusca, Lucian Pintilie, Ioana Pintilie, Adelina Carmen Ianculescu
Corresponding authors: Adelina Carmen Ianculescu and Ioana Pintilie
Study: Influence of grain size on electrical conductive properties and thermally activated transport phenomena in a complex experiment/theoretical model approach in dense nanostructured Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3 și Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 ceramics
The paper will be submitted for publication to the Journal of the European Ceramic Society (Impact factor: 6.364, Article influence score: 0.762) or Ceramics International (Impact factor: 5.532, Article influence score: 0.552).
Presentations to international conferences: 1 invited, 2 oral (in the grant topic, with acknowledgments PN-III-P1-1.1-PD-2019-0739)
1 Downscaling to the critical dimension for stability of the ferroelectric phase in BST ceramics
Authors: R. E. Pătru, M. Botea, C.-A. Stanciu, V.-A. Surdu, R.-D. Truşcă, B. S. Vasile, M. Udrea, I. Pintilie, A.-C. Ianculescu, L. Pintilie
Oral: ICPAM-13, 12th International Conference on Physics of Advanced Materials, September 24-30, 2021, Sant Feliu de Guixols, Spain
2 Low and high field electrical properties of dense fine-grained ferroelectric ceramics prepared via sol-gel method
Authors: Roxana Elena Patru, Catalina-Andreea Stanciu, Georgia Andra Boni, Lavinia Petronela Curecheriu, Nadejda Horchidan, Vasile-Adrian Surdu, Bogdan Vasile, Roxana Trusca, Liliana Mitoseriu, Adelina-Carmen Ianculescu, Ioana Pintilie, Lucian Pintilie
Oral: Electroceramics XVIII, Ceramics in Europe, 10-14 Iulie 2022, Krakow, Polonia.
3 Size-effects in fine-grained BST ceramics: preparation and functional properties
Authors: Roxana Elena Patru, Catalina-Andreea Stanciu, Georgia Boni, Nadejda Horchidan, Lavinia Petronela Curecheriu, Vasile-Adrian Surdu, Bogdan Vasile, Roxana Trusca, Liliana Mitoseriu, Adelina-Carmen Ianculescu, Ioana Pintilie and Lucian Pintilie
Invited: International Workshop on Advanced Materials and Applications, 28-29 October 2022, Iasi, Romania.
Roxana Elena Patru
email: roxana.patru@infim.ro
(+040) 0767 029 290
PROJECTS/ NATIONAL PROJECTS
Copyright © 2026 National Institute of Materials Physics. All Rights Reserved