Highly conductive and transparent metallic electrodes for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes
Project Director: Dr. Silviu POLOSAN
Summary:
The project describes the manufacture of transparent metal electrodes for electroluminescent diodes, which allow the improvement of charge transport through multilayer OLED structures and the increase of light emission due to the electroluminescence obtained on both sides. As a novelty, the application of a patent based on low-energy electron irradiation of metal surfaces facilitates the obtaining of transparent anodes with improved electrical conductivity by decreasing the roughness, using the nanozonal melting of metal films under the action of an electron beam. Regarding the transparent cathodes, the project proposes a new strategy of electrodes with low mechanical extraction work, using alloys between alkaline-earth metals and metallic silver. Ag-Mg compositional optimization for cathodes with uniform distribution and optimal Ag/Mg ratio represents the second novelty of this project. This fact implies obtaining thin films as good quality alloys using thermal co-evaporation and comparing them with those obtained by vacuum thermionic arc deposition.
Objectives:
1. Depositing thin silver films by the thermionic arc method and thermal evaporation in a vacuum.
2. Irradiation of thin silver films with low-energy electrons, and modification of the irradiation parameters in accordance with the objectives of the project (increasing the electrical conductivity of thin films).
3. Comparison of the electrical conductivity of these films before and after irradiation with low energy electrons.
4. Improving cathodes by using Mg-Ag alloys for an optimal charge injection in OLED structures.
5. Construction of OLED structures with optimized metal electrodes and determination of their operating parameters, as a functional OLED demonstrator.
Brief presentation of the results obtained within the project
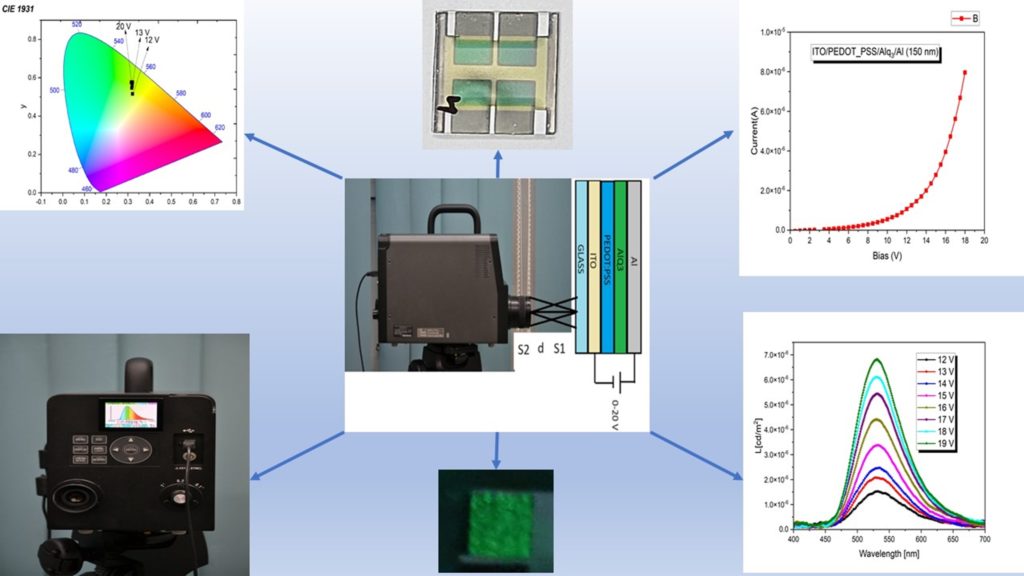
- Obtaining 22-35 nm thick transparent silver cathodes leads to an increase in emission efficiency by 35-40%. This transparency allows the emission of light to be obtained through cathodes and not only through anodes as happens in current classical devices.
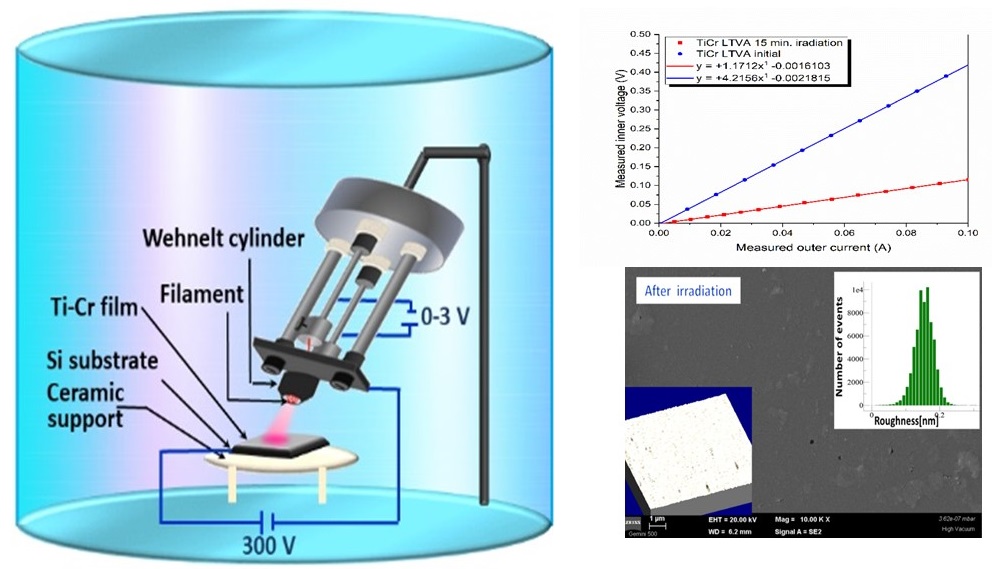
2. Electron irradiation-crystallization of the film induces better electrical conductivity and uniformity that ensures a better charge injection in the diode. Thus, an increase in electrical conductivity by up to 65% is ensured simultaneously with an approximately 3-fold decrease in the roughness of the films from 45-50 nm to 16 nm.
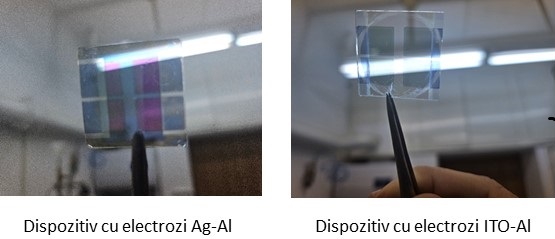
3. Obtaining alloys with variable workfunction, depending on the composition of the alloy, by the vacuum thermionic arc method assisted by laser which, in the case of MgAg alloys, induce an workfunction of electrons of 4.23 eV, slightly higher than that of of 3.68 eV magnesium films, but with much better chemical stability and superior electrical conductivity.4.Obtaining metallized fiber type transparent cathodes with up to 90% transparencies and high electrical conductivities. The high transparency of metallized fibers induces a non-uniform charge injection in electroluminescent devices, which considerably reduces the quantum emission efficiency of these devices. The performances of transparent metallic films are shown below.
Coordinator-NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF MATERIALS PHYSICS, Magurele, Romania
Dr. Silviu Polosan- director de proiect silv@infim.ro
Dr. Iulia Corina Ciobotaru - cercetator corina.ciobotaru@infim.ro
Dr. Constantin Claudiu Ciobotaru - cercetator claudiu.ciobotaru@infim.ro
Dr. Ionut Enculescu -cercetator encu@infim.ro
Dr. Andrei Nitescu-doctorand andrei.nitescu@infim.ro


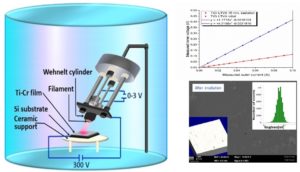
Low energy electron irradiation method.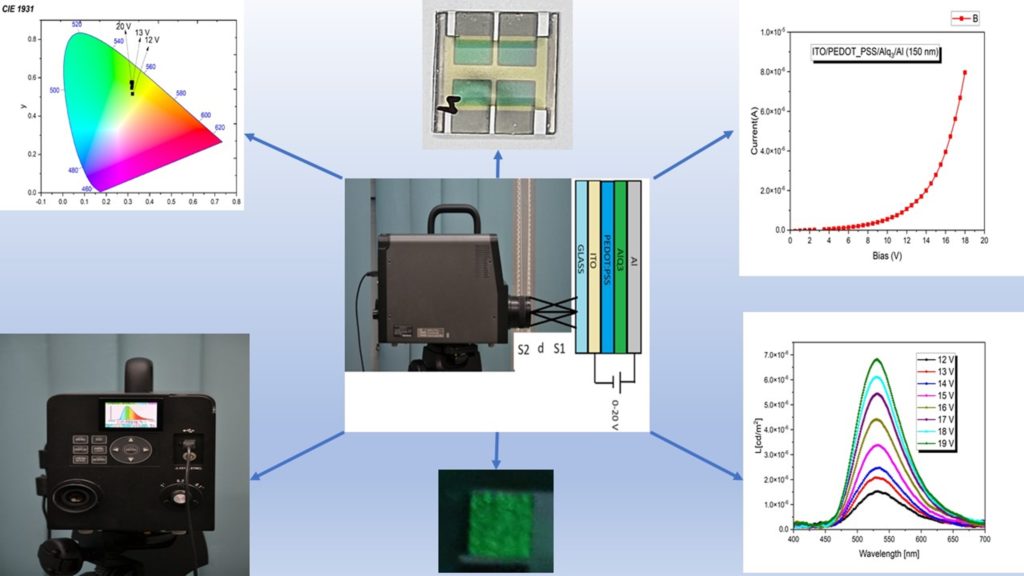
Electroluminescence of OLED devices with transparent electrodes.Summary of stage 1.
a) The installation of thermal evaporation and deposition by thermionic arc has been re-designed so that the thickness of the deposited metal films is monitored with the help of a quartz balance. Also, the evaporators were brought closer with the help of spacers so that the deposition angle is as small as possible, as well as the nacelle-substrate distance, thus ensuring an efficient deposition of the metal films.
b) The thermionic emission process was adjusted by using two DC sources necessary to accelerate the emitted thermoelectrons to:
- Low voltages (0-400 V) and currents of the order of hundreds of microamps for low-energy electron irradiation of metal surfaces. The method was tested on a tantalum metal plate, establishing the main electron irradiation parameters.
- High voltages (0-2 kV, 0-2 A) for the realization of the thermionic arc (TVA), i.e. the deposition of the films in its own plasma. The main deposition parameters (filament current, anodic voltage and current, breakdown voltage and deposition time) were established for silver films deposited on a glass substrate.
c) The vacuum thermal evaporation parameters were established for the silver and magnesium films, by depositing three silver samples of different thicknesses and a very thin magnesium sample.
d) A co-evaporation of magnesium-silver in a ratio of 1:10 was carried out at different evaporation rates, but the preliminary results require refinement of the method to obtain a ratio of 10:1 silver-magnesium.
e) A silver-magnesium co-evaporation was achieved by the modified thermionic arc method with the application of a 532 nm laser beam to homogenize the alloy on the glass substrate, but the ratio was 1:4, a fact that requires additional investigations regarding the preliminary silver mixture and magnesium as well as adjusting the laser power to obtain the desired ratio.
1. S. Polosan , C. C. Ciobotaru , I.C. Ciobotaru , M. Enculescu , D. Iosub, A. Mandes , R. Vladoiu, „Electron Irradiation of Titanium-Doped Chromium Nanostructured Thin Films for Higher Conductive Electrodes”, IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, Vol.21, p. 823-829 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNANO.2022.3227366.
2. Vladoiu, R.; Mandes, A.; Dinca, V.; Matei, E.; Polosan, S.
"Synthesis of Cobalt–Nickel Aluminate Spinels Using the Laser-Induced Thermionic Vacuum Arc Method and Thermal Annealing Processes"
Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3895. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12213895.
3.I. C. Ciobotaru , M. Enculescu , S. Polosan, I. Enculescu, C. C. Ciobotaru, „Organic Light-Emitting Diodes with Electrospun Electrodes for Double-Side Emissions”, Micromachines, 14(3), 543 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030543.
4. R.Vladoiu, A. Mandes, V. Dinca, M. Tichy, P. Kudrna, C.C. Ciobotaru, S. Polosan, „Versatile techniques based on the Thermionic Vacuum Arc (TVA) and laser-induced TVA methods for Mg/Mg:X thin films deposition-A review” Journal of Magnesium and Alloys, 12, 3115-3134 (2024) (IF=17.2), (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jma.2024.08.012)
"EFFICIENT METAL ELECTRODES FOR ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DIODES"-invitedS. Polosan, R. Vladoiu,A. Nitescu, C.C. Ciobotaru, C.I. Ciobotaru, E. Matei, V. Ciupina,
Conferința Științifică Națională de Toamnă a Academiei Oamenilor de Știință din România, ediția a 34-a „Știință pentru o societate sănătoasă”, 21-23.09.2023.
"ADVANCED MATERIALS BASED ON MAGNESIUM TYPE MgX-X=Ti,Ag,Zn, OBTAINED BY THE LTVA METHOD"-invited
R. Vladoiu, V. Ciupina, V. Dinca-Balan, A. Mandes-Vaduva, S. Polosan
Conferința Științifică Națională de Toamnă a Academiei Oamenilor de Știință din România, ediția a 34-a „Știință pentru o societate sănătoasă”, 21-23.09.2023.
- "ORGANIC ELECTROLUMINESCENT DIODES: PRESENT AND FUTURE"-invited
S. Polosan,
Conferința Științifică Națională de Primăvară a Academiei Oamenilor de Știință din România, 24-25.05.2024.
- "COMPLEX MAGNESIUM-BASED NANOSTRUCTURES DEPOSITED BY LASER-INDUCED VACUUM THERMIONIC ARC (LTVA) FOR HIGH-EFFICIENCY ELECTRODES"-invited R. Vladoiu, A. Mandes, V. Dinca, S. Polosan, M. . Tichy, P. Kudrna, 2023, 21st IBWAP, Constanta, Romania.
- "PROPERTIES OF MAGNESIUM ZIRCONIUM THIN FILMS MADE BY TVA AND LTVA TECHNIQUES"-poster
R.Vladoiu,V.Dinca, A. Mandes, S. Polosan, E. Matei, B. Mardare, IBWAP 2023, Constanta, Romania.
1. S. Polosan, A. Nițescu, A. Mandeș, V. Dincă, R. Vladoiu „Aliaje magneziu-argint pentru catozi utilizați in tehnologiile diodelor electroluminescente”, Nr. cerere OSIM A/00752 din 28 Noiembrie 2023
2. S. Polosan, I.C. Ciobotaru, C.C. Ciobotaru, E. Matei „Electrozi metalici de argint iradiați cu fascicule de electroni de energie joasa si procedeu de obținere”, Nr. cerere OSIM A100754 din 28 Noiembrie 2023
Project PED726/2021 evaluated with the qualification:
EXCELLENT Dr. Silviu Polosan, Doctor of Physics
Scientific Researcher I
National Institute of Materials Physics
Laboratory of Multifunctional Materials and Structures
Phone: +40-(0)21-2418 268
email: silv@infim.ro
PROJECTS/ NATIONAL PROJECTS
Copyright © 2026 National Institute of Materials Physics. All Rights Reserved